Activated carbon equipment of production line
What is activated carbon?
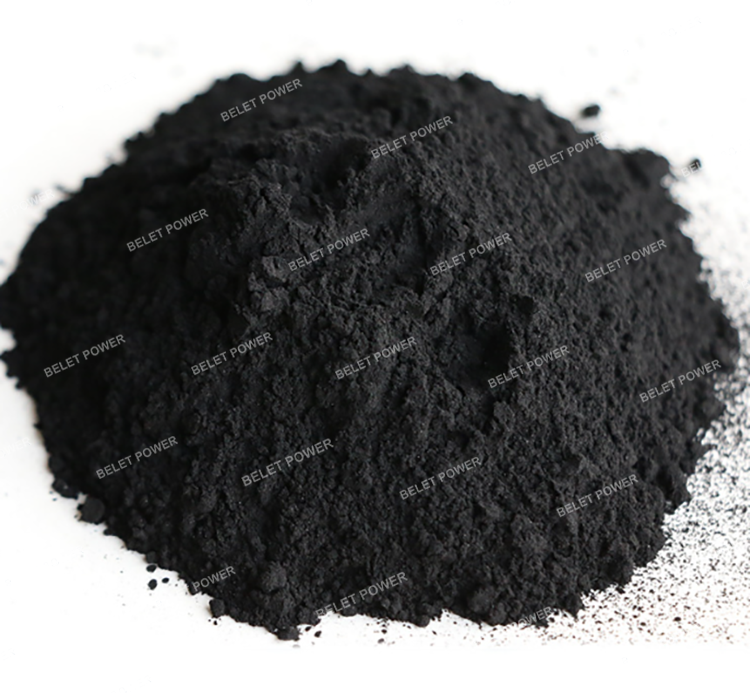
Activated carbon is a porous solid carbon with a large specific surface area and strong adsorption capacity! It possesses many characteristics that other types of carbon materials do not have, such as thermal stability, chemical inertness, thermal process ability and pore structure. It is also an important inorganic material and is widely used in many fields, with water treatment and air purification being the most common applications. Now, as society's environmental protection requirements become increasingly strict, activated carbon, as an important environmentally friendly material, is being increasingly applied in industrial production.

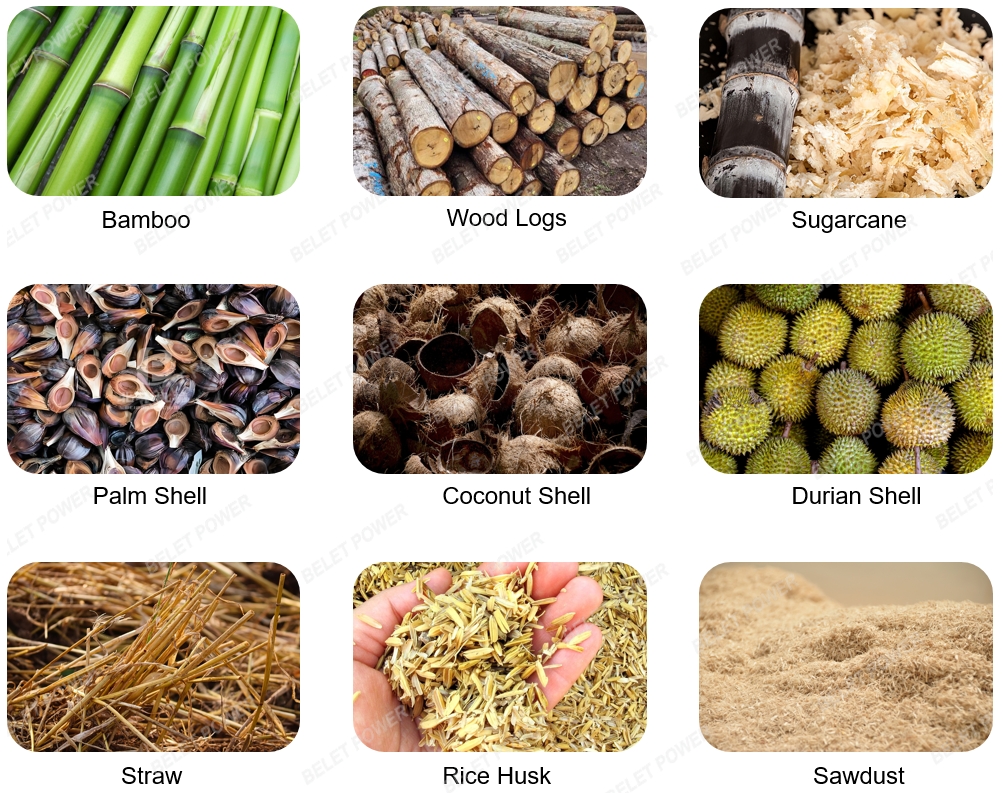
Applicable raw materials
Charred material particles ranging from 0.2 to 10 mm, including palm shells, various fruit shells, wood, rice husks, hard wood materials, bamboo and sugarcane residue.

Introduction to Production Line Equipment
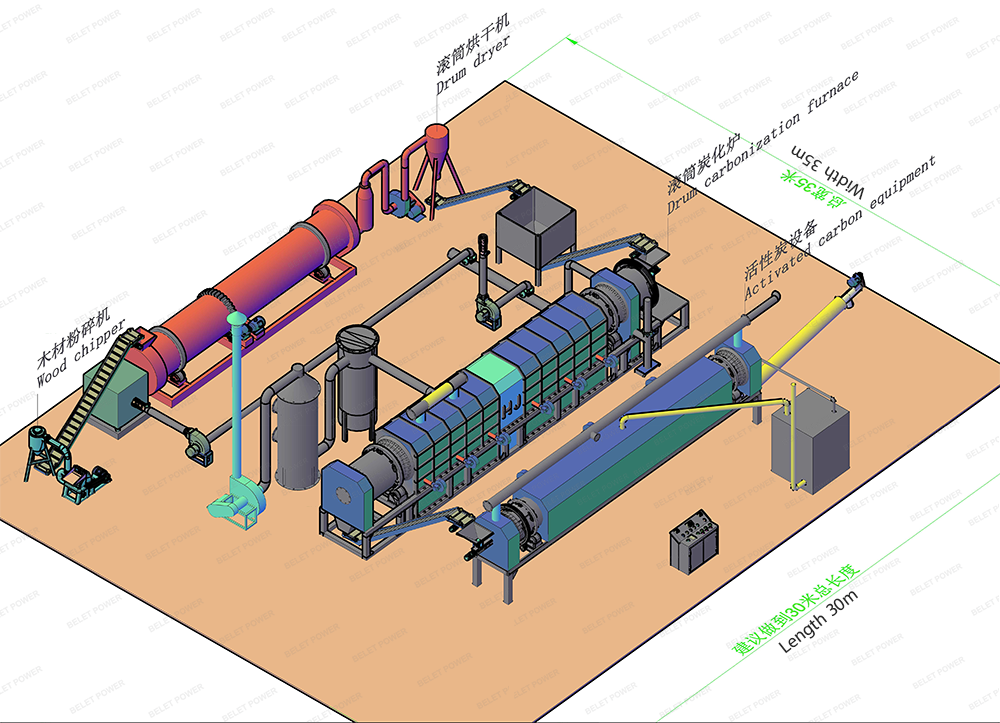
At present, there are mainly two methods for preparing activated carbon from activated carbonized materials in activated carbon production: one is the internal heating type, and the other is the external heating type. The mainstream equipment is the internal heating activation devices, such as the Sleep furnace and the internal heating rotary furnace. However, external heating activation devices are currently rare on the market. This is mainly because although the previous external heating activation devices were relatively inexpensive and easy to operate, they required additional heat sources to maintain the activation temperature, resulting in higher production costs.

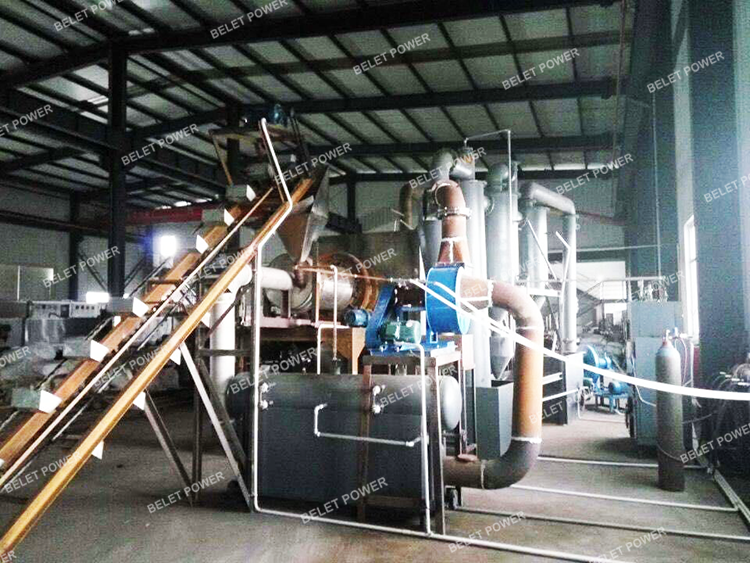
The main part of our activated carbon production line still adopts the external structure of the external heating rotary furnace. Besides, it also includes a steam generator, a system for collecting the combustible gases (such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide) in the activation device and using it for heating, a labyrinth design at the inlet and outlet ends, the setting of the steam supply pipes in the activation device, the exhaust pipes for the combustible gases generated during the activation process, two self-suction type open flame burners for external heating, and one of the burners is used to bring the carbonized material and water vapor to the reaction temperature before the activation process begins, generating stable combustible gases, and then this type of burner is stopped and another burner for burning the combustible mixed gas extracted from the activation device is turned on, thus achieving a production mode without the need for an external heat source.

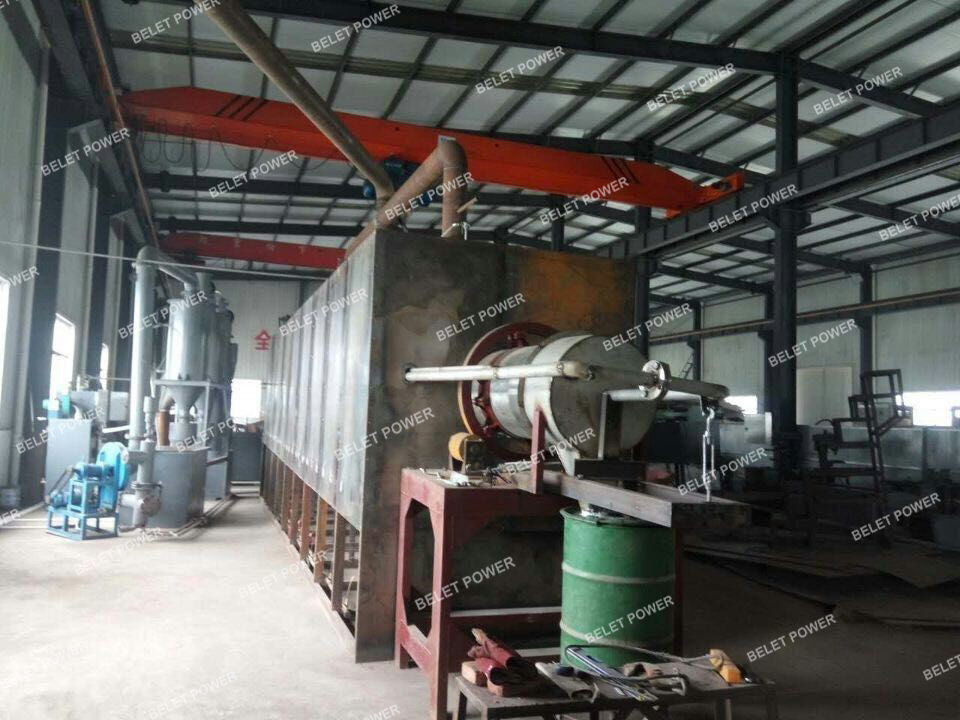
This production line is equipped with two sets of steam generators. One of the main steam sources is a biomass pellet steam generator, which only costs about 30% of the electricity cost. The steam temperature is approximately 140℃. This steam pipeline passes above the rotary kiln. The exhaust gas from the combustion of the kiln (around 300℃ with certain heat content) heats the steam again, and the steam enters the activation rotary tube and can reach 260℃, further improving the activation efficiency and energy utilization. The other is a waste heat to hot water steam generator that provides a small amount of steam directly entering from the discharge port. It exchanges heat with the carbonized particles in the cooling zone, cooling the carbonized particles and increasing the steam temperature entering the furnace tube, thereby improving the activation efficiency.
The water of the constant-temperature water circulation indirect cooling device is connected to the biomass steam generator. The hot water after indirect heat exchange with the carbonized particles enters the steam generator to generate steam, reducing energy consumption.

Our activated carbon equipment production line has a history of over 15 years. Once an order is confirmed, we will provide a detailed drawing of the specifications.
Uses of Wood-Based Activated Carbon
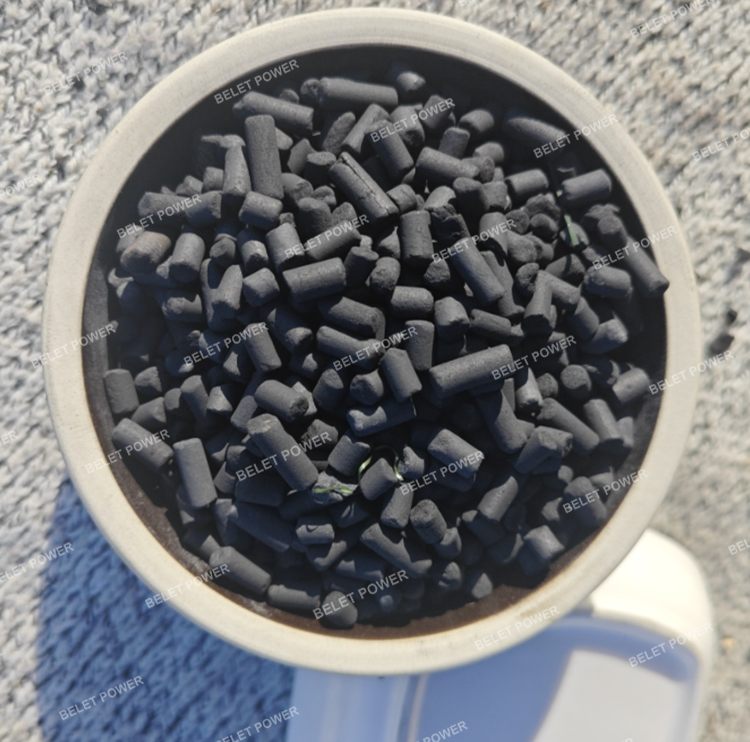

1. Gas phase adsorption
2. Recovery of organic solvents (recycling of benzene-based gases such as toluene, xylene, and acetone in the acetate fiber industry, and the recovery of acetone in viscose short fiber production, etc.)
3. Removal of harmful gases and impurities with high adsorption and desorption properties, thereby significantly increasing the recovery rate of solvents. Removal of impurities, decolonization, purification, deodorization, wastewater removal, and impurity removal for products such as glutamic acid and its salts, lactic acid and its salts, citric acid and its salts, wine, seasonings, animal and plant proteins, biochemical products, pharmaceutical intermediates, vitamins, antibiotics, etc.








